Why Budgerigars (Budgies) Originated in Australia and Their Journey to Domestication

Budgerigars, also known as budgies, are small parrots native to Australia. They have a long history in the country, with evidence of their existence dating back thousands of years.
These birds have evolved to thrive in the harsh Australian environment, with their vibrant plumage and distinctive chirping making them popular pets worldwide.
In Australia, budgerigars have been domesticated for centuries, with breeding programs aimed at producing a wide range of colors and patterns. Today, they are one of the most popular pet birds globally, known for their intelligence and social nature.
Origins of Budgerigars in Australia
Originating from the vast and diverse landscapes of Australia, budgerigars are small, colorful parrots renowned for their intelligence and social nature. These birds have a long history in the Australian wilderness, where their unique adaptations have allowed them to thrive in various environments. Budgerigars, also known as budgies, are well-adapted to the harsh conditions of the Australian outback, where they've evolved to withstand high temperatures and scarcity of water sources.
In the Australian wilderness, budgerigars have developed specialized features that help them survive. Their ability to efficiently extract moisture from seeds enables them to thrive in arid regions where water is scarce. Additionally, their vibrant plumage serves as both camouflage and a means of attracting potential mates.
The unique adaptations of budgerigars reflect their long-standing presence in the Australian landscape. Understanding these adaptations not only sheds light on their evolutionary history but also highlights the importance of preserving their natural habitats for future generations to appreciate and study.
Unique Features of Australian Environment

The unique features of the Australian environment have played a crucial role in shaping the evolution and adaptation of budgerigars. This includes its diverse climate, rich flora and fauna, and geographic isolation.
The varying climates across Australia have influenced the different colorations and behaviors seen in budgerigars today.
The abundance of native vegetation and wildlife has provided a rich source of food and shelter for these small parrots, contributing to their survival and eventual domestication.
Australian Climate Diversity
Australia's diverse climate features a wide range of unique environmental conditions that have shaped the evolution of its flora and fauna. The continent's climate diversity has influenced various species, including the iconic budgerigar, in fascinating ways.
Key points to consider include:
- Climate Adaptation: Australian species have developed specific adaptations to survive in diverse climates.
- Breeding Habits: The fluctuating climate patterns in Australia have influenced the breeding habits of many native species.
- Evolutionary Advantages: The varied climates have provided evolutionary advantages to species, promoting genetic diversity.
- Color Variations: The range of climates has also contributed to the distinctive color variations seen in many Australian fauna.
This intricate relationship between climate diversity and wildlife showcases the resilience and adaptability of Australia's unique ecosystem.
Flora and Fauna
Within the unique ecosystem of Australia, the diverse flora and fauna exhibit remarkable adaptations to the continent's varied environmental conditions. Australian bird diversity is exceptional, with over 800 bird species, including the iconic budgerigar. These birds have evolved unique characteristics to thrive in Australia's diverse habitats, from the arid outback to coastal regions.
Ecosystem interactions in Australia are intricate, with plants and animals co-evolving over millions of years. For instance, many Australian plants rely on specific bird species for pollination and seed dispersal, showcasing the interconnectedness within the ecosystem. The continent's flora, such as eucalyptus trees and acacias, have adapted to survive in nutrient-poor soils and harsh climates, further illustrating the resilience of Australian flora and fauna.
Geographic Isolation
Geographic isolation in the Australian environment has played a pivotal role in shaping the evolution and distinct characteristics of its diverse flora and fauna. This isolation has led to unique features that have influenced the evolutionary history and genetic diversity of species within Australia.
Specific to the budgerigars, this isolation has contributed to their behavioral adaptations and their ability to thrive in their ecological niche. The Australian environment's distinct characteristics, such as harsh climatic conditions and limited resources, have compelled species like budgerigars to develop specialized traits for survival.
This has resulted in a rich tapestry of biodiversity that showcases the intricate interplay between geography, environment, and the evolution of species.
- Evolutionary history and genetic diversity
- Behavioral adaptations and ecological niche
- Unique features influenced by isolation
- Survival strategies in harsh conditions
Adaptations for Survival in the Outback

With their vibrant plumage and keen eyesight, budgerigars have developed remarkable adaptations to thrive in the harsh conditions of the Australian Outback. Over millions of years, these small parrots have evolved impressive evolutionary adaptations to overcome the environmental challenges of their arid homeland. One of the key adaptations is their ability to efficiently extract moisture from the seeds they consume, allowing them to survive in regions where water is scarce.
Budgerigars have also developed special respiratory adaptations that help them cope with the hot and dry Outback climate. They're capable of adjusting their breathing rate and efficiently conserving water, enabling them to thrive in environments where other bird species would struggle to survive.
Additionally, their cryptic coloration and small size provide them with effective camouflage against predators, allowing them to blend seamlessly into the arid landscape. These adaptations showcase the resilience and resourcefulness of budgerigars in the face of the challenging Outback conditions.
Role of Budgies in Indigenous Culture
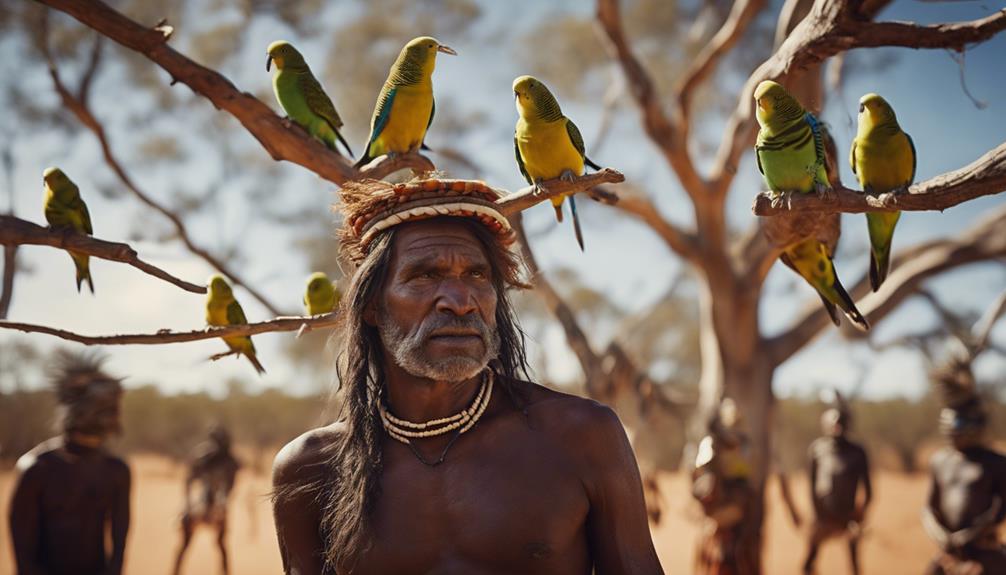

Budgerigars, also known as budgies, hold a significant place in Indigenous Australian culture. These vibrant birds aren't only admired for their beauty but also play a crucial role in spiritual practices and rituals.
The close connection between Indigenous communities and budgies dates back centuries, highlighting the deep-rooted cultural significance of these feathered creatures.
Cultural Significance of Budgies
Engrained in the cultural fabric of indigenous communities, budgerigars have long held a revered status for their symbolic representations and spiritual significance. These vibrant birds have inspired various aspects of indigenous culture, serving as a source of artistic inspiration and embodying deep cultural symbolism.
- Artistic Inspiration: Budgerigars' colorful plumage and playful nature have been a muse for indigenous artists, influencing traditional art forms and designs.
- Symbol of Connection: Budgies are seen as a symbol of connection to nature and ancestral spirits in indigenous beliefs.
- Ceremonial Importance: The presence of budgerigars in ceremonies signifies blessings and good fortune.
- Storytelling: Budgies feature prominently in indigenous stories, carrying moral lessons and cultural teachings through generations.
Spiritual Connection With Budgies
Indigenous cultures have long revered budgerigars for their deep spiritual connection and symbolic importance, embodying a profound relationship with nature and ancestral beliefs. Budgies hold significant spiritual symbolism as bird companions, believed to serve as messengers between the physical and spiritual realms.
In many indigenous cultures, budgerigars are seen as animal guides, guiding individuals through life transitions and offering protection and wisdom. The intricate patterns and vibrant colors of budgerigars are often interpreted as signs from the spiritual world, carrying messages of hope, resilience, and renewal.
Through their graceful flight and melodious chirps, budgies are thought to bring peace and harmony, fostering a sense of interconnectedness with the natural world and promoting spiritual growth among those who observe and care for them.
Discovery by European Explorers

European explorers first encountered the vibrant plumage and playful nature of budgerigars during their voyages to the Australian continent in the late 18th century. These early encounters sparked a fascination among the explorers, leading to a deeper exploration of these captivating birds.
- Early Encounters: European explorers were amazed by the colorful plumage and melodic chirps of the budgerigars, documenting their findings in journals and reports.
- Indigenous Interactions: Indigenous Australians had long interacted with budgerigars, considering them an integral part of their environment and culture.
- European Fascination: The unique characteristics of budgerigars, such as their ability to mimic sounds and their social nature, intrigued European explorers and naturalists.
- Conservation Efforts: As the popularity of budgerigars grew in Europe, conservation efforts were initiated to protect these birds in their natural habitat.
The discovery of budgerigars by European explorers paved the way for further study and eventual domestication of these charming birds.
Transition to Popular Domestic Pets

The captivating allure of budgerigars quickly captured the interest of enthusiasts, propelling these colorful birds into the realm of popular domestic pets. Known for their playful and social behavior traits, budgerigars are highly trainable, making them ideal companions for those seeking interactive pets. With proper training, these intelligent birds can learn to mimic words and perform tricks, adding to their charm as household pets.
In terms of health care and nutrition, budgerigars require a balanced diet consisting of seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables to thrive. Owners should ensure access to clean water and a variety of perches and toys to keep them mentally stimulated. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential to monitor their health and address any potential issues promptly.
The transition of budgerigars from wild birds to beloved domestic pets highlights the adaptability and companionship they offer to individuals and families worldwide. As their popularity continues to grow, understanding their unique needs and providing proper care remains crucial for a harmonious relationship between humans and these delightful avian companions.
Global Spread of Budgerigar Ownership
With budgerigars gaining popularity as domestic pets, their ownership has spread globally, establishing them as cherished companions in households around the world. The global spread of budgerigar ownership has had significant implications, including:
- Economic Impact: The demand for budgerigars has led to a thriving industry surrounding their breeding, sale, and care, contributing to the economy in various countries.
- Breeding Programs: Dedicated breeding programs aimed at producing budgerigars with specific traits have emerged worldwide, ensuring a diverse and healthy population of these birds.
- Conservation Efforts: While budgerigars are widely bred in captivity, efforts to protect their wild populations in Australia and other regions are ongoing to maintain genetic diversity and preserve their natural habitats.
- Wild Populations: Conservationists work to monitor and protect wild budgerigar populations, studying their behaviors and habitats to ensure their survival in the face of environmental challenges.
The global ownership of budgerigars highlights the intersection of human fascination with these birds and the need for conservation and responsible breeding practices to safeguard their future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Budgerigars Be Found in the Wild Outside of Australia?
Budgerigars, also known as budgies, are primarily found in the wild in Australia. While they have been introduced to other parts of the world, wild populations exist mainly in their native habitats. Conservation efforts aim to protect these birds.
What Is the Average Lifespan of a Budgerigar in the Wild Versus in Captivity?
In the wild, budgerigars have an average lifespan of 5-8 years due to predators and harsh conditions. In captivity, with controlled environments and proper care, they can live 15-20 years, benefiting from a more stable and secure lifestyle.
Are There Any Specific Predators That Pose a Threat to Budgerigars in the Wild?
In the wild, budgerigars face threats from predators like birds of prey, snakes, and feral cats. These predators exploit the budgerigar's small size and swift movements in their natural habitats, showcasing intricate predator-prey dynamics.
How Do Budgerigars Communicate With Each Other in the Wild?
Budgerigars communicate with vocal interactions, displaying intricate social behaviors. They use chirps, whistles, and calls to convey messages about feeding habits, nesting rituals, and establishing hierarchy within their flock, essential for their survival in the wild.
Are There Any Known Medicinal or Nutritional Benefits Associated With Consuming Budgerigars in Traditional Indigenous Cultures?
In some traditional indigenous cultures, budgerigars are valued for their cultural significance and dietary benefits. They are used in medicinal practices and are believed to provide essential nutrients, showcasing the deep connection between nature and health.











